Now - 19:40:06
Azimuthal projection: definition, types and classification
To transfer the three-dimensional object, you must use a special projection. In cartography there are many types of projections for different regions of the earth's surface. One of them is azimuthal projection.
What is the projection?
A Projection – a way of transferring three-dimensional image on a flat surface. The transfer is carried out with strict observance of mathematical laws and rules to reduce the influence of distortion.
The Distortions are, in any case, different can be just their types. Depending on the purpose the purpose of the resulting flat image, used some type of projection that is performed by their own rules and gives one of the distortion types.
Projections are the most widely used in the preparation of maps and plans earth surface of different sizes. For mapping, there are also the types of projection, each of which has a different purpose.
Cards
Even in ancient century, humans began to create images of the Earth. The information on them was incomplete, distorted and sometimes even wrong. The continents on ancient maps were too large, the shapes of the banks were untrue. Since the mapping process has changed a lot, improving their methods, but to completely get rid of the distortion and impossible.

Devoid of distortion model of the Earth is a globe. It more accurately reflects the shape and size of the earth, passing on its surface in a valid form. The globe, however, is three-dimensional figure, and not always easy to perform special calculations and solve practical problems. Besides, it is very inconvenient for transportation. Flat map better suited to these purposes, though it gives less accurate information.
Recommended
"Knowledge is light and ignorance is darkness": the value, meaning and alternatives
There are some sayings that would seem to need no explanation, such as “teaching & ndash; light and ignorance – darkness”. But some still do not understand their meaning. But not only for such people is written by our article. I...
What was invented by Mendeleev for the army. The history and fate of the invention
D. I. Mendeleev was a brilliant Russian scientist-polymath, who made many important discoveries in various fields of science and technology. Many people know that he is the author of “Fundamentals of chemistry" and the periodic law of chem...
The origin of the Slavs. The influence of different cultures
Slavs (under this name), according to some researchers, appeared in the story only in 6 century ad. However, the language of nationality bears the archaic features of the Indo-European community. This, in turn, suggests that the origin of the Slavs h...
The Types of projection
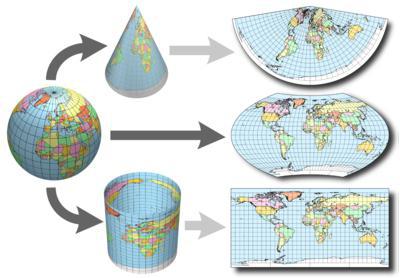
Today in cartography there are three main types of projection depending on the types of meridians and Parallels. Each of them, in addition, there are subtypes according to the location of projection planes and the nature of the distortion.
- Cylindrical projection. If you imagine that the globe can surround a plane close to the Equatorial line representing the shape of a cylinder, it is possible to define the variety. When projecting the meridians on the paper will be straight lines, converging at one point the poles, and the Parallels – straight, parallel to each other. The least distortion will be observed at the equator and greatest – near the poles.
- Conic projection. Is formed at the contact plane in the form of a cone with a globe. In this case, Parallels will be shown on the map in the form of concentric circles and the meridians are their radii. The least distortion will also occur in places of contact of the plane with the ball on the Ground, but the biggest – in places of the greatest removal.
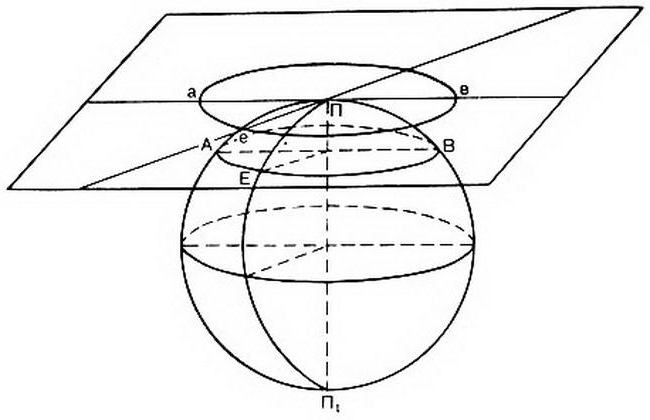
- Azimuthal projection. Is formed at the contact plane of the earth. When projecting a plane can not only touch, but intersect the Earth, which is also one type of azimuthal projection. In this case, Parallels also will be drawn as concentric circles, distant from each other, and the meridians are their radii. The angle between adjacent meridians will be of the same magnitude as the difference between the longitude of the specified location.
There are also conditional species, externally similar to one of three groups of projections, but performed by other mathematical laws. These include the polyconic, pseudocylindrical, multiple.
Azimuthal projection
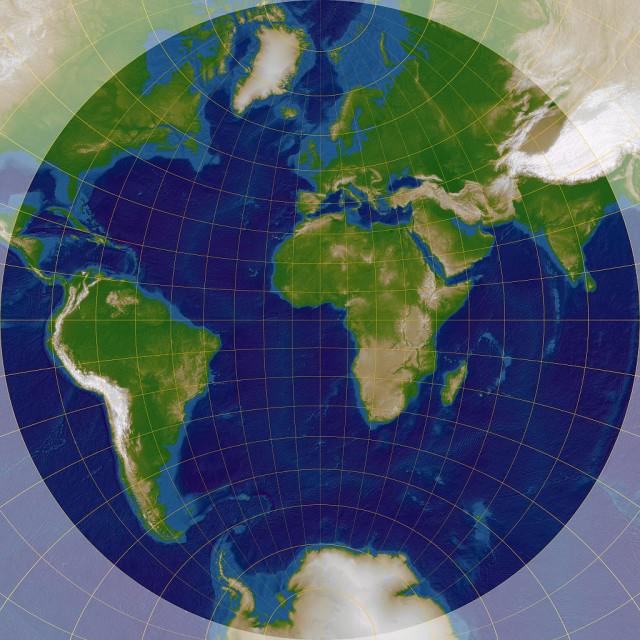
Azimuthal projection of the Earth is widespread because of preservation without distortion of the azimuth lines on the resulting picture plane. The point from which the projection is called a point of view. The point of contact of the globe with a plane is called a tangent point.
On the map there are lines with identical values of distortion. They are named Sokolov. On the image obtained in the azimuthal map projection, Sokoly have the form of concentric circles. The distortion increases as one moves away from the contact points between the plane and the globe. As a result, the greatest accuracy is very touch point.
Characteristics
Azimuthal projection can be performed in various ways depending on the purpose of the resulting maps. The methods vary by the type of distortions arising from the transfer of the image onto the plane.
- Isometric-projection, which preserves the area, dimensions, lengths of objects, but changes the angles and shapes. Most often used to solve applied problems related to the calculation of dimensional values.
- Conformal-projection, leaving almost unchanged the angles of the objects, but distorts their sizes.
- Equidistant-projection, which are distorted and the angles and area of the feature, but the zoom remains on the main path. Used mainly in Geoinformatics and computer systems.
- Arbitrary – projectionwhich can distort all of the parameters to different degrees depending on the goals and purpose of the map. Used for various purposes, for example, in the marine case to determine routes and trajectories. On such maps the continent of Eurasia may have the same size as Australia.
Subtypes projection
In Addition to the types of distortion, there are other elements perform the projection. Depending on this, there are subgroups of types of azimuthal projections.
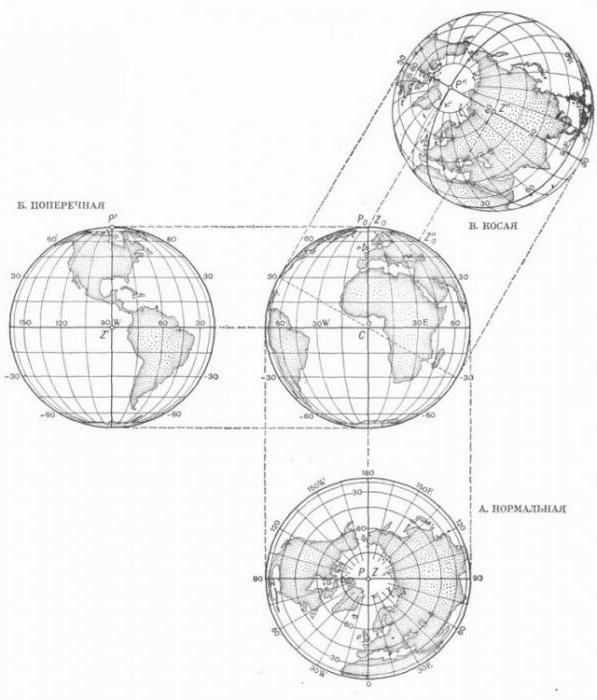
Depending on the position of tangent or secant plane of projection are:
- The Arctic – the picture plane touches the globe at the point of one of the poles.
- Cross – picture plane touches the globe in place the line of the equator.
- Oblique – picture plane touches the globe at any other location (in latitude from 0 to 90 degrees).
Depending on the location of the viewpoint are distinguished:
- Central & ndash; a point from which the projection is located in the centre of the earth;
- Stereographic – point of view is the distance from the tangent point at a distance equal to the diameter of the globe;
- External – a point of view removed from earth for any possible distance;
- Orthographic-perspective doesn't exist or it was removed at an infinite distance, and the projection is performed using parallel lines.
The Most common of them are the azimuthal projection of Lambert, polar, and transverse projection.
Projection Lambert
The azimuthal projection of Lambert performed in different parts of the Earth. It allows you to keep low distortion of the square and their relationships, but strongly changes the angles and shapes. The scale on a map in the direction of meridians and Parallels will change in different ways. With the distance from the center horizontally, it will decrease 0.7 times, and vertically-to grow 1.4 times.
On the map, made in such projection the equator and Central Meridian are drawn straight lines, perpendicular to each other. Other meridians and Parallels are curved lines.
The Projection can be performed to create maps of polar regions (the normal projection) and to create maps of all other regions (Equatorial and oblique projection).
The Projection may cover quite large areas, so it is used for mapping entire continents, regions, and hemispheres. It is widely used to create maps of the Western and Eastern hemispheres due to the small values of distortion. Also used to project onto the plane of the continent of Africa. The disadvantage is the large distortions that occur off the coast of Eurasia.
Card made in the projection of Lambert, are commonly used in geography textbooks.
Polar projection
Earth's Polar regions, it is impossible to perform with minimal distortion in a cylindrical or conical projection. Picture plane, as a rule, almost does not concern the Arctic and Antarctica, and this area is mapped with the very large errors of sizes and shapes. However, the polar azimuthal projection allows to create an exact image of the polar zones on a flat surface.
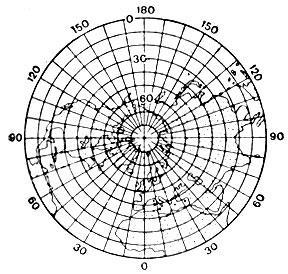
In this case, the tangent point coincides with the North or South pole or is in close proximity to them. The meridians on the map are depicted as straight lines emanating from the middle of the card. Parallels are concentric circles, the distance between which increases as the distance from the touch point.
Transverse projection
Transverse azimuthal projection is used to create maps of the Western and Eastern hemispheres.
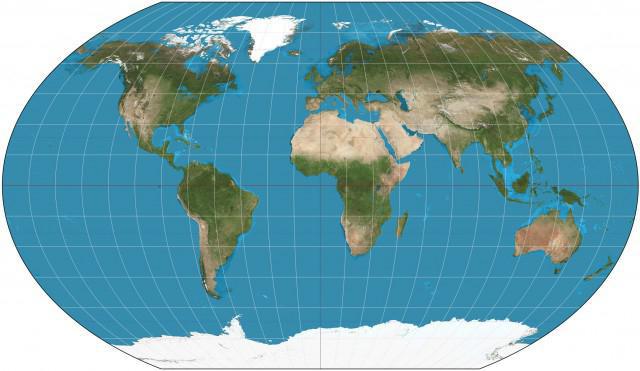
The Smallest distortion in this case arises at the equator and surrounding areas, but the biggest – near the poles. Therefore, to create maps of poles, it is desirable to use a different projection with the goal of creating a more accurate information.
Projection
Azimuthal projection is one of the most important map projections. It is suitable for mapping large areas of the earth's surface, and to create maps of individual countries or continents. This is very important due to the fact that other ways of transferring images onto a plane – the cylindrical and conical variants – are only suitable for hemispheres or the entire Earth.
Select the view
Select the type of projection depends on such factors as:
- The Location, shape and size of the mapped region.
- The Purpose and the goal of creating a card.
- The Type of the applied problems, the solution of which will be made using the card.
- Feature selectable projection – the magnitude of the distortion, and the shape of meridians and Parallels.
The significance of the factors may be determined arbitrarily depending on conditions and purpose.
Article in other languages:
PT: https://tostpost.com/pt/educa-o/13048-azimutal-naya-proje-o-defini-o-tipos-e-classifica-o.html

Alin Trodden - author of the article, editor
"Hi, I'm Alin Trodden. I write texts, read books, and look for impressions. And I'm not bad at telling you about it. I am always happy to participate in interesting projects."
Related News
Method of analysis of hierarchies
For the adoption of certain decisions of administrative nature, and to tentatively predict likely outcomes, a person entrusted with decision-making, often faced with considerable number of interdependent elements, the system which...
A feudal society. Class of feudal society
Feudal society was considered almost universal form of management for Eurasia. Most of the peoples that inhabited it, passed through this system. Next we shall consider what was feudal society. CharacteristicsDespite some changes ...
Yellow star: the examples, the difference in color of stars
Any star - yellow, blue or red - is a red-hot ball of gas. A modern classification of bodies is based on several parameters. These include the surface temperature, size and brightness. The color of stars visible on a clear night, ...
What is the Luggage? Value, synonyms and interpretation
Plane, train, car. What are these nouns? Today we analyse what is the Luggage. Consider the meaning, synonyms and, of course, different interpretations. Because Luggage – it's not only suitcases.SignificanceMost people do no...
What is the rational nomenclature
the Name of his rational nomenclature derived from Latin ratio "reason". This system was first allowed to give a logical name organic compounds based on their belonging to a particular class. She was replaced by trivial names, whi...
Where to get the best education: 32 Lyceum (Vologda)
32 high school (Vologda) can rightly be called one of the oldest educational institutions of the city. In 2002, the Lyceum celebrated its hundredth anniversary, birthday.HistoryAs already mentioned, in 2002 the Lyceum celebrated t...




















Comments (0)
This article has no comment, be the first!