Now - 09:55:47
Fungi: General characteristics and significance
Very detailed information about the organisms give tutorials on the subject of "biology" (6th grade). General characteristics of fungi, however, are the subject of entire books and treatises. And it is not surprising to study them very interesting.
Fungi whose common characteristic is presented in this article, the ecological and trophic indicators - heterotrophic eukaryotes with extremely osmotrophy type of food. It's Oprahdivision clearly separates them from other organisms on the space taken up by the biota. General characteristics of fungi suggests that osmotrophy method of feeding due to morpholocal, physiological, and biochemical features.
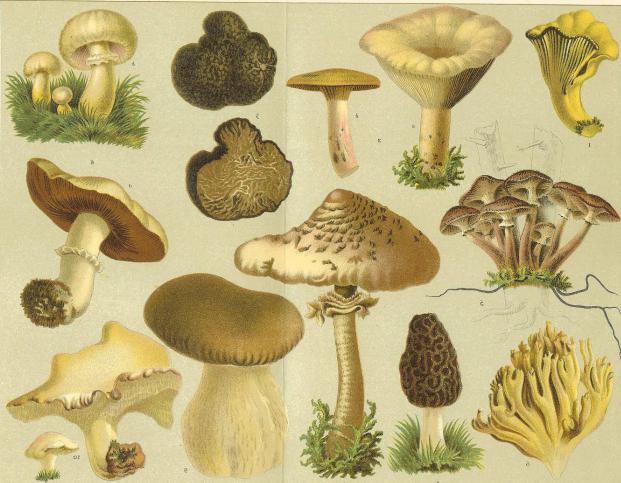

The Vegetative body of fungi
The Vegetative body of most fungi is a highly timewietlenie threads (hyphae) with unlimited growth, the totality of which is called the mycelium, or the mycelium. Mycelium usually immersed in the substrate (soil, plant tissue, animal droppings, vegetable remains, etc.), and such features of its structure make it possible to extract from it the nutrients the entire body with ectomus.
Organic matter in these substrates are mainly in the form of high molecular weight polymers (proteins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids) that do not pass through the cell covers. Therefore, the fungi whose common characteristic we are interested in, isolated in the substrate depolymerase enzymes that cleave Primery to oligo - and monomers able to be transported into the cells. If animals have digestive enzymes to stand out inside the gut, the fungi they stand out, and then the mushroom GIFA can be likened to the inside out colon.
Recommended
"Knowledge is light and ignorance is darkness": the value, meaning and alternatives
There are some sayings that would seem to need no explanation, such as “teaching & ndash; light and ignorance – darkness”. But some still do not understand their meaning. But not only for such people is written by our article. I...
What was invented by Mendeleev for the army. The history and fate of the invention
D. I. Mendeleev was a brilliant Russian scientist-polymath, who made many important discoveries in various fields of science and technology. Many people know that he is the author of “Fundamentals of chemistry" and the periodic law of chem...
The origin of the Slavs. The influence of different cultures
Slavs (under this name), according to some researchers, appeared in the story only in 6 century ad. However, the language of nationality bears the archaic features of the Indo-European community. This, in turn, suggests that the origin of the Slavs h...
Propagation of mushrooms
Complete immersion of the mycelium in the substrate limits their racessettlements in space. Therefore, their reproductive organs are nominated on the substrate surface or rise above it to spread in the air or (if the substrate is in the water) the aquatic environment. Many fungi (macromycetes) of the spore-bearing bodies of large, well visible to the naked eye (rising above Pochhowl pileate mushrooms growing on a tree the fungus). Other fungi (micromycetes) are small bodies of spores, their structure can be seen only under the microscope, but the mass development they form colored deposits in the form of mold on various substrates.
Kingdom fungi

Phylogenetic construction show that ecomorph "mushrooms" is not a homogeneous monophyletic group and is divided into two phyla (kingdoms). A large part, called "true mushrooms" (audacity), monophyletic and is actually the Kingdom fungi (Fungi). The smaller part, called the "mushroom-like organisms" (pseudomycelia), is included along with some algae in the Kingdom Stramenopila, which gruperois in two division — the Oomycota (the oomycetes) and Labyrinthulomycota (net of SLIsevici). On the basis of this division is built General characteristics of fungi. Pileate mushrooms, as you can see, is only a part of all their diversity.
Primary and secondary metabolites
All metabolites are divided into primary and secondary. Primary metabolites essential for growth of the organism and is indispensable. It's nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, coenzymes, lipids, etc. are built-cellular organelles-nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, cell wall and MEMabusive structures that have mushrooms. General characteristics primary metabolites is that their deposits the cell uses as a source of nutrition and energy. Secondary metabolites required for adaptations orgaISM to the conditions of life. They can occur in some species and absent in others. Unlike primary, secondary metabolites — that is, as a rule, low molecular weight compounds.
Proteins
Structural proteins are part of cell wall, membrane structureTur, of chromosomes, of which built elements of the cytoskeleton-microtubules and microfilaments. Enzyme proteins provide all of the intracellular Proprocesses and interaction with the environment.
Carbohydrates
Structural polymeric carbohydrate - based cell walls, which are mushrooms. General characteristics of these carbohydrates, in terms of chemical composition allows to divide them into three groups: glucose, other monosaccharides and carbohydrates covalently linkeding with peptides (glycoproteins).
Polymers of glucose — it glucans, chitine and cellulose. Glucans representationrepresent a linear or branched chain of glucose molecules. They make up the outer layer of the cell wall of most fungi. The chitin molecules of glucose residues connected with AMInagrodami (zaminirovanii), which, in turn, is attached the remains of acetic acid (azetilirovanny). Molecules "stitched" to each other branched molecules and other polysaccharides constitute the solid skeleton of the cell wall. Cellulose is found in all the studied oomycetes, of which it constitutes about 10% of the mass of the cell wall. Long believed that it is not true fungi, but now shown its presence in the wall of some yeasts (genus Ophiostoma).
The other Polymers of the monosaccharides(mannose, galactose, etc.), called in higher plants the hemicellulose, do not occur in all groups of fungi. Especially a lot of polymers of mannose-mannan — in the cell walls of yeastJay. Apparently, such a composition wall provides budding better than glucan.
Finally, the General characteristics of fungi may be added the fact that in their cell walls, like plants, contains a lot of polysaccharides linked to protein molecules — peptidoglycan, mannoprotein etc. They form the middle layer of the multilayer cell walls and play an important role in maintaining the structural integrity of cell and its metabolic processes with the environment.
Spare carbohydrates
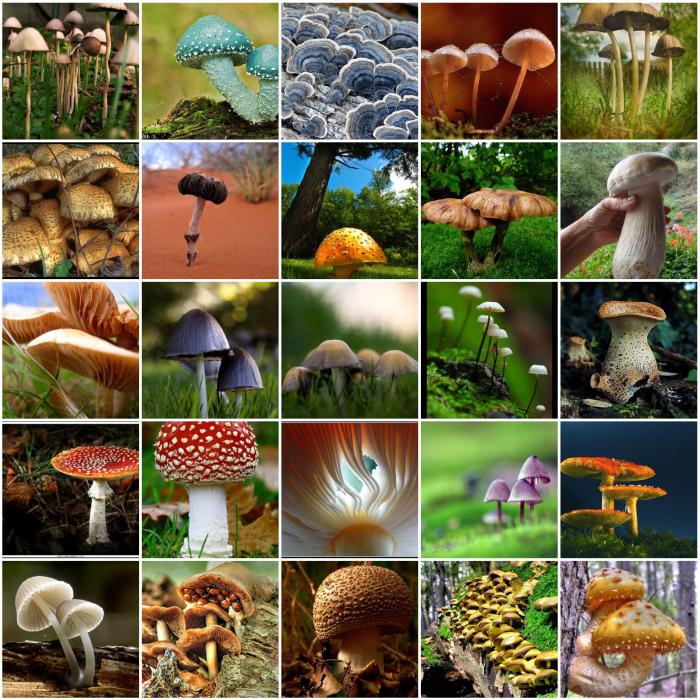

This article provides a fairly detailed General characteristics of fungi. 6 grade school is the time when we first familiarized themselves with these organisms in biology lessons. We offer you to deepen the knowledge and to study them in more detail. Let us turn to the description of spare carbohydrates.
Fungi are not detected primary spare PolishReid, inherent in higher plants and many algae — starch. Glucose is eumycetes stored as glucan, which is close to the animal starch glycogen. In addition to glucans in mushrooms have other spare coalwater, some characteristic of the fungi Kingdom. It is primarily the disaccharide trehalose. For a long time trehalose were found only in fungi, why it is often called — of mycosis. Now it is found in some higher plants as minor compounds. Trehalose plays an important role in the adaptation of fungal cells to stress and the regulation of osmotic processes. The fungal cell also contains SharePort — mannitol, sorbitol, xylitol, etc.
Lipids
The Lipids (esters of glycerol with monocarboxylic acids with an unbranched aliphatic chain) are an important spare of Prodoctari, they are deposited in the cell in the form of droplets of fat. Mushroom charth a high content of polyunsaturated (having several double bonds in the aliphatic chain) fatty acids such as linolenic — with three, and arachidonic — with four double bonds. In the form of phospholipidou (United ether bond with phosphoric acid) lipids are essential components of cell membranes. A major role in the creationInstitute of membrane structures are also lipids sterols, giving MEMwounds strength. In contrast to cholesterol, a 27 carbon atoms in the molecule (C-27), and phytosterols (P-29) plants, the main fungal Sterol-ergosterol (C-28).
Secondary metabolites: pigments
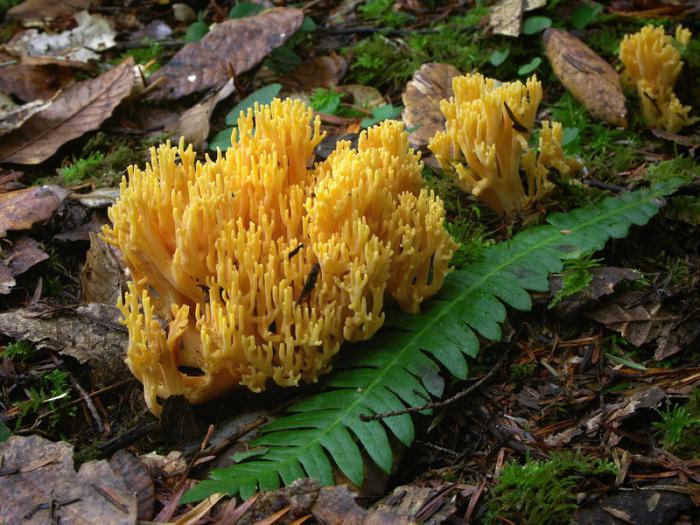

Mushrooms are devoid of photosynthetic pigments, but produce a large number of compounds, coloring and mycelium propagative bodies or the substrate. On the chemical nature of most of the pigments refers to terpenoids (carotenoids) or to aromatic compounds. They perform a variety of functions. So, the orange carotene derivatives induce the flow of the sexual process in fungi immunity; dark greennye and black phenolic pigments of Aspergillus are deferred only to the SPOroosnam unit, which, in contrast to substrate mycelium, formed in air, and in disputes for protection from ultraviolet light; dark-colored melanin deposited in the cell walls, making them so onness.
Toxins and antibiotics
Many fungi produce compounds toxicing for other organisms that are often mentioned when compiled General characteristics of fungi (class 6 textbook or Handbook for the University). Substances that are toxic to the microorganisms,called antibiotic, toxic to plants — phytotoxins, toxinsing to animals and humans — the mycotoxin. Some metabolites GrisBOV, being toxic to different groups of organisms (microorganisms and plants, plants and animals), have a complete action. Antibiotics are synthesized by many soil dwelling fungi, which have to compete for nutritional substrates to other microorganisms. Their chemical nature and mechanism of action are diverse. So, antibiotics-penicillins and cephalosporins inhibit cell wall synthesis in bacteria, trichothecene — the synthesis of protein in eukaryotic microorganisms, griseofulvin — mitosis.
Phytotoxins and mycotoxin
The Phytotoxins secreted by the fungi in the tissue of infected plants, tUte death of plant cells, whichwhich then become easy tobull of the parasite. Toxins inhibit the enzymatic processes in cells forthrough the world of plants (for example, tentacin fungus Alternaria inhibits photosynthetic phosphorylation) the highly strong membranotropic effect and affect the transport of substances thRES of the membrane, transmembrane transport of ions (fusaria acid, fusicoccin, etc.).

Mycotoxins are divided into two groups — toxins microscopic GrisBOV (micromycetes) and toxins of macromycetes fungi with large fruit bodies. The first is especially dangerous fungi infecting vegetable products used as food. For example, the sclerotia of ergot alkaloids accumulate (heterocycles containing nitrogen), which notrvno nerve agent poisons. They are not destroyed inhlebopechkeNII, so the bread baked from flour mixed with ground sclerotia, are extremely dangerous. Its use can cause severe poisoning, often with fatal outcome. Another parasite of cereals — the causative agent of Fusarium head blight of. Fusarium is a fungus that secretes into the grain terpenoid toxins also cause serious poisoning (the bread made from the infected by Fusarium flour, popularly called "drunk bread", as it caused dizziness, vomiting and other symptoms, reminiscent of strong ALCOthan poisoning).
Food mushrooms
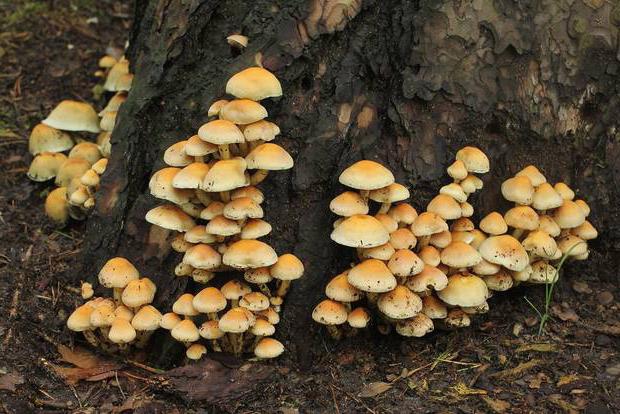

Currently, quite a lot of information about their accumulated food science biology. General characteristics of fungi from this point of view the following. The power of most fungi occurs at the expense of the plants, so they have active enzymes which decompose the structural and spare Polishinformation about in living plants and plant residues. These are the pectinases, ruchausie polygalacturonase acid (pectin) into low molecular weight oligoglucosamine, xylanase, cellobiase and cellulose destroying cellulomemory and hemicellulose — the main carbohydrate components of cell walls of plants, amylase, eroding starch, etc. Second after cellulose by weight component of plant cells — the lignin, which is a threedimensional polymer of aromatic rings. Especially a lot of it in lignified cells. Lignin — the persistent vegetative polymer, and only mushrooms (mainly derevorazrushayuschie tinder) are enzymes lignate, destroying it. Mushrooms-parasites affecting the skin of animals and humans (skin, hair, feathers), secrete enzymes that destroy the protein keratin, of whichcerned they are built.
Most of these enzymes for energy EconomicsMIA synthesized by the cells is not constant, but only in the presence in the environment of the relevant substance (for example, if in the environment there, pection, the pectinase is not synthesized). They are not constitutive, and subject to substrate induction. In addition, they are not formed if the environment is a blend of nutrients with a more favourable energy compoundsmargin exchange (catabolite). For example, the end product of the destruction of the mAtion of polysaccharides — glucose, therefore, in the environment, which in addition of pectin or cellulose contains glucose, pectinases and cellulases are not produced by progwhiz Inc .. are. Hardly it is expedient to produce complex chemical processes to obtain glucose if it's already available in the growth environment. Such regulation is called catabolic repression.
Asexual reproduction
Continuing the topic, as "General characteristics of fungi", briefly describe features of reproduction. Asexual reproduction in these organisms may be mobile and notmotile spores. Zoospores forms a small number of fungi, aquatic and terrestrial, which have a distinctly genetic link with watermi. Structure of flagella in zoospores of oomycetes and hififreak similar to that described for Ajrapetovym algae, and chytrids would be consideredRen in the description of this group. Most species of fungi reproduce immobile spores, indicating their very ancient landfall. Spores can be formed endogenously in sporangia (sporangiospores) or exogenous (conidia). Endogenous spores are released only afterdisruption of sporangia that usually happens when it is wet. Usually the sporangia are formed a large number (thousands) of spores, however, somewhich species form small sporangia (sporangiola), which is only a few spores (sometimes one). In the latter case, the shell sporangia and spores may grow together, and then endogenous to the dispute functions as Exogene. This is evidence of the primary occurrence of endogenous spores, which were the precursors of exogenous.
Sexual reproduction
The Most common type of sexual process, with the most simple — a merger of the two not differentiated into gametes Vegetapositive cells, called somatogamy. This type of sexual process characteristic ascomycete yeast, basidiomycetes and many other GrisBOV. Sometimes it occurs even without cell fusion, simple fusion of the nuclei inside the cell. More complicated sexual process precedes isolation of the sections of the mycelium of partners (gametangia), which are then merged. This sexual process, gameanyone common to many Zigo - and Ascomycetes. Finally, mushrooms can be found common to other eukaryotic orgaorganisms are gametogonia, i.e. the merger of the specialized gametes.
A Classic out - and heterogamy typical for algae, the meetingare only from the lower fungi-the chytrids. Classic oogami fungi non-existent. Even the oomycete, so named due to the presence of aences they have oogami not have male gametes (sperm or spermaries), and oocytes in oogonia without their own cell walls and the nameNY oosphere. In some species of Ascomycetes have a oogonium (but not female gametes ova, i.e. representing gametangia), but the absencethere is antheridia, so the fertilization happens in a vegetative gifoi. Other Ascomycetes and basidiomycete rust fungi are a husbandcal gametes — the nectar, but not female gametes, and sometimes gametangia (spermatogonia). In some species the nectar are dual function — male gametes and spores asexual reproduction(conidia).
Conclusion
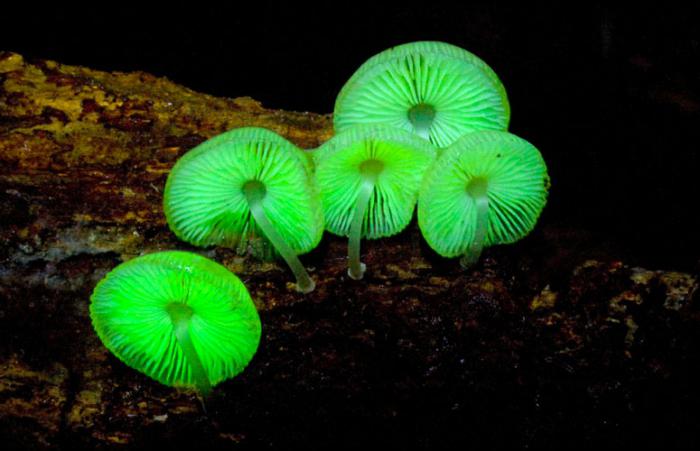

General characteristics of fungi: nutrition and respiration, spore reproduction - all this is of great interest to nature lovers. This is a unique organisms that are neither plants nor animals. Opening the textbook the theme "General characteristics of fungi" (grade 7), you learn that they constitute a separate Kingdom. The other kingdoms are animals, plants, viruses and bacteria. The theme "General characteristics and value of mushrooms" contained in school textbooks and in this article is only basic information about them. About them written entire books, so to do their study very long. One of the most interesting, in our opinion, is the General characteristic of fungi. Mold is one of the most ancient species on Earth living organisms. She appeared 200 million years ago and thrives in the modern world. Open any school textbook "the Kingdom of fungi. General characteristics" (grade 6) and you will find more information about it.
Article in other languages:
AR: https://tostpost.com/ar/education/10444-fungi-general-characteristics-and-significance.html
BE: https://tostpost.com/be/adukacyya/18757-gryby-agul-naya-haraktarystyka-znachenne.html
DE: https://tostpost.com/de/bildung/18775-pilze-allgemeine-merkmale-und-bedeutung.html
ES: https://tostpost.com/es/la-educaci-n/18789-hongos-caracter-sticas-generales-y-su-valor.html
HI: https://tostpost.com/hi/education/10451-fungi-general-characteristics-and-significance.html
JA: https://tostpost.com/ja/education/10451-fungi-general-characteristics-and-significance.html
KK: https://tostpost.com/kk/b-l-m/18752-sa-yrau-la-tar-zhalpy-sipattamasy-zh-ne-ma-yzy.html
PL: https://tostpost.com/pl/edukacja/18726-grzyby-og-lna-charakterystyka-i-znaczenie.html
PT: https://tostpost.com/pt/educa-o/18726-fungos-caracter-sticas-gerais-e-do-valor.html
TR: https://tostpost.com/tr/e-itim/18763-mantar-genel-zellikleri-ve-de-eri.html
UK: https://tostpost.com/uk/osv-ta/18745-gribi-zagal-na-harakteristika-ta-znachennya.html
ZH: https://tostpost.com/zh/education/11212-fungi-general-characteristics-and-significance.html

Alin Trodden - author of the article, editor
"Hi, I'm Alin Trodden. I write texts, read books, and look for impressions. And I'm not bad at telling you about it. I am always happy to participate in interesting projects."
Related News
Pyotr Stolypin: a brief biography
Pyotr Stolypin, a brief biography which is of exceptional interest to any Patriotic historian, was one of the most important political figures in our country in the XX century. About it will be discussed in this article.Pyotr Stol...
The study of Antarctica, scientists from Russia
the Study of Antarctica — a story that illustrates the unrestrained human desire for knowledge of the world, the story about strength of spirit and willingness to take risks. The sixth continent, theoretically located to the...
The calcium oxide. Physical, thermal and chemical properties. Application.
calcium Oxide – the crystalline compound of white color. Other names for this substance-quicklime, calcium oxide, “terabit”, “quicklime". Calcium oxide, the formula of which is CaO, and a product of in...
College of geodesy and cartography MIIGAiK: address, admissions, specialties, reviews
Many applicants seeking to enter such professions, which are now popular. However, there are people who want to get some unusual or infrequently encountered profession, but very important and interesting. Corresponding to such req...
As the vocabulary of the Russian language: advice
the Great Russian language! Studies of modern linguists show: there are about two hundred thousand words. However, the average Russian uses in everyday life not more than three thousand vocabulary. There are many methods how to im...
the Achilles ' heel-idiom denoting the weakness, the vulnerability of any company or person. It can be a personality trait, a feature which spoils the life of, or imperfection in the organization of the business – all that a...





















Comments (0)
This article has no comment, be the first!