Now - 16:05:23
Cells-macrophages. What it is and what they have the functions
In this article we will consider the mechanism of formation of immunity, that is, properties of the body to protect its cells from foreign substances (antigens) or pathogens( bacteria and viruses). Immunity can be generated in two ways. The first is called humoral immunity and is characterized by the production of specific protective proteins-gamma globulins, and the second – cell, which is based on the phenomenon of phagocytosis. It is due to the formation in the organs related to the endocrine and immune system, special cells: lymphocytes, monocytes, basophils, macrophages.
Cells-macrophages: what is it?
Macrophages, together with other protective cells (monocytes) are the main structures of the phagocytosis-the process of capture and digestion of foreign substances or pathogens that threaten the normal functioning of the body. Described the protective mechanism was discovered and studied by Russian physiologist I. Mechnikov in 1883. It was established that cellular immunity include phagocytosis – a defensive reaction, which protects the genome of the cells from the damaging effects of foreign agents, called antigens.
To understand the question: macrophages - what are these cells? Recall their cytogenes. These cells are derived from monocytes that have left the bloodstream and entered a tissue. This process is called diabetes. The result is the formation of macrophages in the parenchyma of the liver, lungs, lymph nodes and in the spleen.
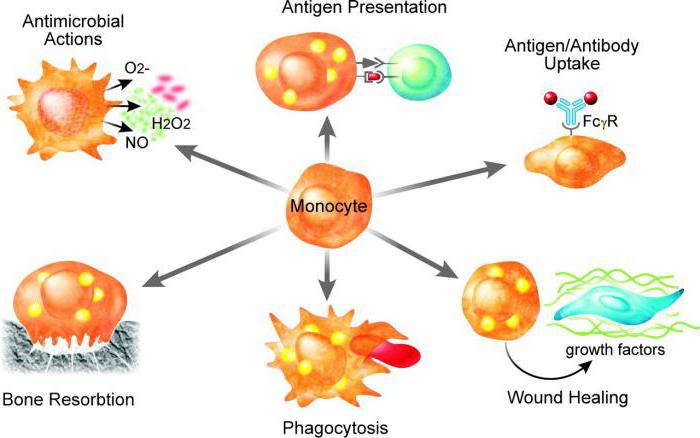
For Example, alveolar macrophages are the first contact with a foreign substance trapped in the pulmonary parenchyma through specific receptors. Then these immune cells engulf and digest antigens and pathogenic organisms, thus protecting respiratory organs from harmful pathogens and their toxins, as well as destroying particles of toxic chemicals trapped in the lungs with a portion of the air during inhalation. In addition, it was proved that the level of immune activity of alveolar macrophages similar to the protective blood cells-monocytes.
Recommended
A tablet from worms – the relevance of the application for the person
How relevant today, drugs against worms in humans? What kind of creatures these worms, what are modern methods of treatment? We will try to answer these questions, since ignorance in this area is undesirable. Imagine a mummy, which is misleading in k...
What to do if you cracked skin on hands?
Each of us at least once in a lifetime encounter with a small, but very, when the crack the skin on the hands. At this time there are wounds of different sizes, which hurt and cause inconvenience, especially when in contact with water or detergents. ...
Spray Macho man - the key to a proper relationship between the two spouses
Male impotence is a pathological condition associated with abnormal physiological capacity of the penis to reginout and bring sexual partner pleasure in bed.sex impotenceimpotence may not men to pass unnoticed – it usually spoils his nervous sy...
Features of the structure and functions of immune cells
The Phagocytic cells have specific cytological structure, which determines function of macrophages. Their cell membrane is able to form pseudopodia used to capture and coat foreign particles. In the cytoplasm are many digestive organelles-lysosomes, providing a lysis toxins, viruses or bacteria. There are also mitochondria that synthesize molecules of adenosine triphosphate, which is the main energetic substance of macrophages. There is a system of tubes and tubules & ndash; endoplasmic reticulum with belokrinitski organelles-ribosomes. Necessarily the presence of one or more nuclei, often of irregular shape. Multinucleated macrophages are called symplast. They are formed as a result of intracellular karyokinesis, without division of the cytoplasm.
Types of macrophages
Consider the following, using the term “macrophages” that it is not one kind of immune structures, and heterogeneous tsitsikama. For example, there are fixed and loose protective cages. The first group includes alveolar macrophages, phagocytes parenchyma and cavities of the internal organs. Fixed immune cells present in the composition of osteoblasts and lymph nodes. Depositing and blood-forming organs - liver, spleen and red bone marrow also contain fixed macrophages.
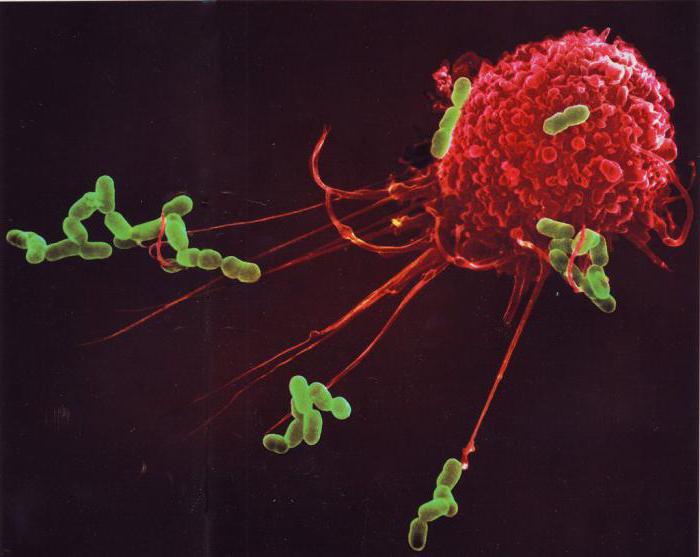
What is cell-mediated immunity
The Above-mentioned types of phagocytes are combined in a highly efficient macroregions system, which directly provides the ability to resist pathogens and toxic agents and destroy them by capturing and digesting. Furthermore, cellular immunity is antibodies produced by T and b-lymphocytes that bind with surface antigens of viruses, bacteria and intracellular parasites: Rickettsia and chlamydia.
Peripheral immune blood-forming organs, represented by the tonsils, spleen and lymph nodes, forming a functionally unified system, responsible for hemopoiesis and immunogenesis.
The Role of macrophages in the formation of immune memory
After the contact of the antigen with cells capable of phagocytosis, the latter “remember” biochemical profile of the pathogen and to respond with antibody production on its re-entry into a living cell. There are two forms of immunological memory, positive and negative. Both are the result of the activity of the lymphocytes generated in the thymus, the spleen, the plaques of the walls of the intestine and lymph nodes. Among them are derived lymphocytes-monocytes cells and macrophages.
Positive immunological memory is essentially a physiological rationale for the use of vaccination as a method of prevention of infectious diseases. As memory cells rapidly recognize antigens in the vaccine, they immediately respond to the rapid formation of protective antibodies. A negative phenomenon of immune memory is taken into account in transplantation to reduce rejection of transplanted organs and tissues.
The Relationship of the hematopoietic and immune systems
All of the cells involved with the body for the implementation of its protection from pathogens and toxic substances that are formed in the red bone marrow, which is hematopoietic organ. The thymus gland, or thymus, are related to the endocrine system, the function of the basic structure of the immune system. In the human body and red marrow and thymus are, in essence, the main organs of immunogenesis.
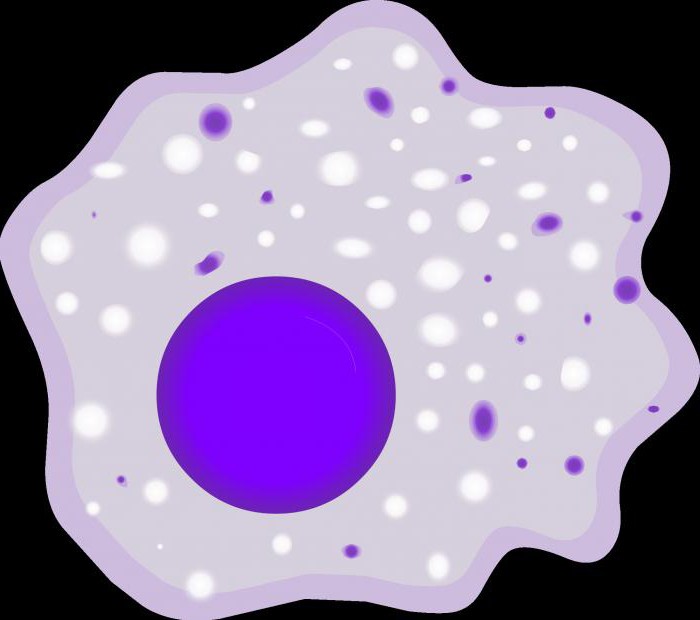
The Phagocytic cells to destroy pathogens that usually is accompanied by inflammation in infected organs and tissues. They produce a special substance-the platelet-activating factor (PAF) increases permeability of the blood vessels. Thus, a large number of macrophages from the blood enter into the presence of the pathogen and destroy it.
Having Studied the macrophages ' cells, in which organs they are produced and the functions - we have seen that along with other types of cells (basophils, monocytes, eosinophils), they are the main cells of the immune system.
Article in other languages:
PL: https://tostpost.com/pl/zdrowie/10726-kom-rki-i-makrofagi-co-to-jest-i-jakie-maj-funkcje.html
PT: https://tostpost.com/pt/sa-de/10723-c-lulas-de-macr-fagos-o-que-e-o-que-eles-possuem-fun-es.html

Alin Trodden - author of the article, editor
"Hi, I'm Alin Trodden. I write texts, read books, and look for impressions. And I'm not bad at telling you about it. I am always happy to participate in interesting projects."
Related News
Step-by-step treatment boil at home
Often treatment boil is produced at home using traditional medicine. And it's worth noting that this method almost always gives a positive result.Before you begin self-deliverance from this affliction, you should find out what the...
Alveolitis: treatment, causes, symptoms, complications and description
Probably not a secret that dentists are not only children but also some adults. Therefore, decide on a tooth extraction for many is a rather difficult decision. And well, if the process goes smoothly, and after 7-10 days, the woun...
What if there are many harmful and fatty foods?
the Question of what happens if there are many, excites virtually everyone who can't resist a huge number of tasty and nutritious food. It is worth noting that habit much to eat can lead not only to obesity but to many other healt...
How is trichomoniasis: ways of transmission and methods
Trichomoniasis referred to an infectious disease that affects the urogenital system.this Happens due to infection of the organism by the parasite. It's vaginal or vaginal Trichomonas. Infection often leads to vaginitis, proctitis,...
How to treat endometritis at cows?
Endometritis-inflammation, which is manifested on the mucous membrane of the uterus. From the point of view of the reproductive system of cows, the uterus is a very sensitive organ, which often can show inflammation. However, the ...
A trephine biopsy of the breast: results, effects, reviews
Cancer of the breast today are in first place by frequency of occurrence in women of different ages. In order to determine the presence of this disease, a woman needs at the first symptoms undergo a series of examinations that wil...



















Comments (0)
This article has no comment, be the first!