Now - 12:31:25
The structure of the seed. External and internal structure of the seed
During his school course in botany (grade 6) structure of the seed was fairly simple and catchy theme. In fact, this generative organ of the plant was the result of a long evolutionary process and has a complex and unique structure. In our article we consider the features of its structural parts, the structure of dicotyledonous seed, and to determine the biological role of seed plants.
Emergence of the seed in the process of evolution
Plants have not always been capable of seed formation. It is known that life originated in water, and the first plants were just algae. They had primitive structure and reproduce by vegetative parts of the thallus and with the help of specialized motile cells called zoospores. The first people on the land were inifity. They, and their future successors - higher spore-bearing plants, reproduce by means of spores. But for the development of these specialized cells needed water. Therefore, when changing environmental conditions have reduced their numbers.
The Next evolutionary step was the emergence of the seed. It was a huge step forward for the adaptation and dissemination of many types of plants. External and internal structure of the seed determine the reliable protection of the embryo, surrounded by a supply of water and nutrients. And therefore increase the vitality and species diversity of flora on the planet.

The process of forming the seed
Let's Consider this process on the example of a group of plants, which in the modern world is dominant. They are representatives of the division of angiosperms. They form a flower - critical generative organ. Its pistil is the ovule and the anther contain sperm. After the process of pollination, i.e. the transfer of pollen from anther of stamen to stigma of the pistil, the sperm at the germinal tube moving the ovary stamens, where the process of fusion of gametes - fertilization. The result is a fetus. When fusion of the second sperm with the Central cell, the germ is formed in the spare nutrient. It is called the endosperm. Seed completes the construction of durable outer shell. This structure is the basis for the future development of plant body.
Recommended
"Knowledge is light and ignorance is darkness": the value, meaning and alternatives
There are some sayings that would seem to need no explanation, such as “teaching & ndash; light and ignorance – darkness”. But some still do not understand their meaning. But not only for such people is written by our article. I...
What was invented by Mendeleev for the army. The history and fate of the invention
D. I. Mendeleev was a brilliant Russian scientist-polymath, who made many important discoveries in various fields of science and technology. Many people know that he is the author of “Fundamentals of chemistry" and the periodic law of chem...
The origin of the Slavs. The influence of different cultures
Slavs (under this name), according to some researchers, appeared in the story only in 6 century ad. However, the language of nationality bears the archaic features of the Indo-European community. This, in turn, suggests that the origin of the Slavs h...
External structure of the seed
As already mentioned, the outside of the seed is coated with the shell. It's dense enough to protect the embryo inside from mechanical damage, extremes of temperature and penetration of harmful microorganisms. But the color of the seeds varies from black to bright red. Such a structure seed is easy to explain. In some plants the color is for camouflage. For example, the birds are unable to consider them in the soil after planting. Other plants, on the contrary, are adapted for seed dispersal by different animals. Together with the undigested remnants of the food they produce them far outside the natural habitat of the parent plant.

Internal structure of the seed
The Main part of any seed is the embryo. This is the next body. So it consists of the same parts as an adult plant. This is the embryonic root, stem, leaf and pacejka. The structure of the seed of different plants may differ significantly. Most of them have spare nutrients accumulate in the endosperm. Is a shell that surrounds a fetus around, protecting and nourishing it during the whole period of individual development. But there are cases when during the process of maturation and germination of seed it fully consumes the substances of the endosperm. Then they accumulate mainly in the fleshy parts of the embryo. They're called cotyledons. Such a structure is typical, for example, pumpkins or beans. But shepherd's purse nutrients concentrated in the germ tissue of the spine. Different and seeds of various systematic groups of plants.
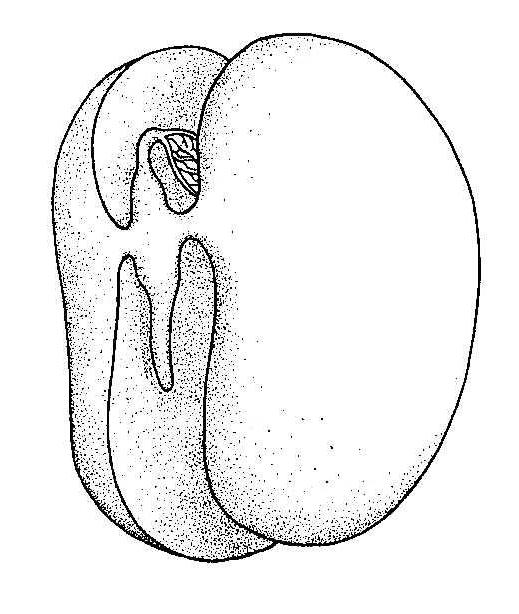
Features of seeds Gymnosperms
External and internal structure of the seed of this group of organisms is characterized by the fact that the process of formation and development of the embryo occurs on the surface of the seed coat. In addition to basic parts, Gymnosperms seeds have wing-like membranous outgrowth. It helps to spread the seeds of these plants using the wind.
Another feature of the seeds of Gymnosperms is the length of their formation. To become viable, it should take from four months to three years. The ripening of seeds occur in cones. This is not a fruit. They are specialized modifications of escape. Some coniferous seeds can be stored in the cones for decades. All this time they remain viable. The seeds hit the ground, the scales of the cones open on their own. They are caught up in the wind, sometimes carrying over long distances. If the bumps are soft, resembling nuts, they appear not to themselves, but with birds. Especially love to eat the seeds of various species of jays. It also contributes to the settling of representatives of the Department of Gymnosperms.
The name given to the systematic unit indicates that the germ of the future plants are poorly protected. Indeed, the presence of endosperm guarantees only the development of the seed. But many bumpsplants open during adverse conditions of development. Once on the soil surface, seeds are exposed to low temperatures and lack of moisture, so not all of them germinate and give rise to a new plant.
Features of seeds of Flowering plants
Compared to the Gymnosperms, in Angiosperms have a number of significant advantages. The formation of seed occurs in ovaries of flowers. This is the most extended part of the pistil, which gives rise to the fruit. In the result, the seeds develop inside them. They krajiny three layers of the pericarp, which differ in their properties and functions. Consider their structure, for example the drupe of the plum. Leathery outer layer protects against mechanical damage, ensuring the integrity. Medium is juicy and fleshy. He nourishes and provides the embryo with essential moisture. The inner stiff layer is an additional protection. As a result, the seed has all the necessary conditions for the development and germination, even under adverse circumstances.
Seeds of Monocots
The seed Structure of monocotyledons plants very easy to identify. Their Bud with only one cotyledon. These parts are also called the germinal layer. Monocots are plants of the families Gramineae, and Liliaceae the Onion. If you germinate seeds of corn or wheat, soon on the soil surface of each grain is formed by one leaf. This is the cotyledons. I tried to split a grain of rice into several parts? Of course, it's impossible. All because her fetus is formed only of the cotyledons.

The Seeds of Dicotyledonous plants
The Seeds of Rozotsvetnye families, Solanaceae, Asteraceae, Fabaceae, Brassicaceae, and many other differ somewhat in structure. Even based on the title, you can guess that their embryo consists of two cotyledons. This is the main systematic feature. The structure of seeds of dicotyledonous plants easily seen with the naked eye. For example, the sunflower seeds easily divided into two equal parts. Is it the cotyledons of the embryo. Structure of dicotyledonous seed can be seen on young shoots. Try at home to germinate seeds of the ordinary beans. And you will see two of the carpel which will appear above the earth's surface.
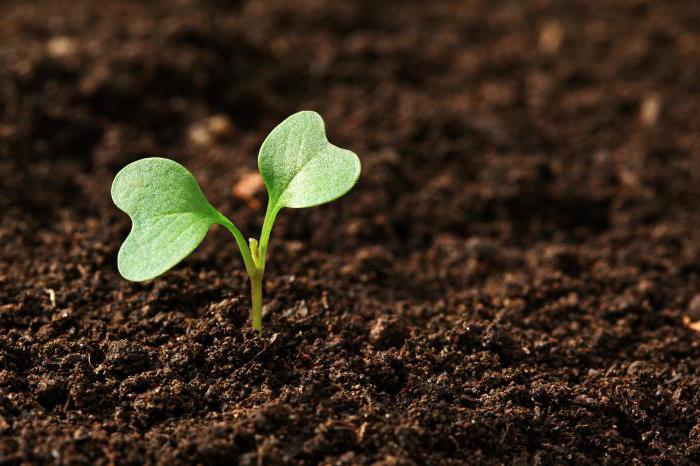

Terms of seed germination
The structure of the seeds of dicotyledonous plants, as well as representatives of other systematic units of this Kingdom of nature, leads to the existence of all necessary substances for the development of the embryo. But needed for germination and other conditions. For each plant, they are completely different. First, it is a certain temperature. For heat-loving plants is 10 degrees Celsius. But the winter wheat starts to develop already at + 1. Water is also necessary. Thanks to her, the seed swells, which accelerates the processes of respiration and metabolism. Nutrients pass into the form in which they can be assimilated by the embryo. The presence of air and sufficient sunlight - two more conditions for seed germination and development of the whole plant, since without them impossible photosynthesis.

Seeds and fruits
Each fruit contains seeds. The structure of seeds of higher plants is almost identical. But the fruit is more diverse. Allocate dry and juicy fruits. They differ in the structure of the layers, which are arranged around the seed. Have juicy one of the layers of the pericarp fleshy sure. Plum, peach, Apple, raspberry, strawberry... These treats are loved by all due to the fact that they are juicy and sweet. From dry fruit pericarp leathery or stiff. Its layers are usually fused into a single, reliably protects the seeds inside. Box poppy pod mustard, caryopsis of wheat have exactly this structure.

The Biological role of the seed
Most of the plants on the planet for reproduction use exactly the seeds. The structure of the seeds of modern plants is the result of a long evolution. These generative organs contain the germ and nutrients to ensure its growth and development even in adverse conditions. Seeds have adaptations for proliferation, which increases their chance of survival and resettlement.
So the seed is the result of the process of fertilization. It is a structure consisting of the embryo, spare substances, and protective of the rind. All the elements perform certain functions due to which group of seed plants to dominate the planet.
Article in other languages:
BE: https://tostpost.com/be/adukacyya/36405-budova-nasennya-zneshnyae-nutranae-budova-nasennya.html
KK: https://tostpost.com/kk/b-l-m/36706-rylysy-ry-yn-syrt-y-zh-ne-shk-rylysy-ry-yn.html
TR: https://tostpost.com/tr/e-itim/33172-yap-tohum-d-ve-i-yap-s-tohum.html
UK: https://tostpost.com/uk/osv-ta/37014-budova-nas-nini-zovn-shn-vnutr-shn-budova-nas-nini.html

Alin Trodden - author of the article, editor
"Hi, I'm Alin Trodden. I write texts, read books, and look for impressions. And I'm not bad at telling you about it. I am always happy to participate in interesting projects."
Related News
Statistics plane crash in Russia for 10 years
the safest form of transport is the plane. Accidents on the road happen more often than the crash of the aircraft. However, the larger the crash. They killed dozens, and even hundreds of people. This is confirmed by the statistics...
An essay on the topic "Compassion". The theme of compassion and mercy
Topics school essays can be very different. Of course, it should match the current curriculum and be aimed at improving grammar, language and speech skills of the child. Equally important, however, is in this respect the education...
Robert the Bruce, king of Scotland: domestic and foreign policy, biography
Scottish national hero Robert the Bruce really deserves the honorary title. His real pride was a hard-fought victory in the fierce battle of Bannockburn. Only thanks to this event Scotia received long-awaited independence, though ...
History, traditions, the capital, the head of state and the state language of Belarus
Belarus – is a country in Eastern Europe. Were formerly part of the USSR, and in 1991 came out of it. Now has several names – Belarus or Belarus. But the official name has been maintained for 25 years – the Repub...
As prefixal-suffixal way words are formed: examples
the Main way of word formation – morphological. It is characterized by the fact that a new word is created by using prefixes, suffixes, the prefixes and the suffixes, drop a significant part of the way addition. So, prefixal...
Geographical position and area of the Crimea in square km
On the border of two climatic zones, where East meets West, offers this unique territory - the Crimean Peninsula. How many people live here today? What features of the nature of the Peninsula can be identified? What is the area of...





















Comments (0)
This article has no comment, be the first!