The importance of the nervous system. The function of the nervous system
Every organ or system in the human body play a role. While they are all interrelated. The importance of the nervous system cannot be overestimated. She is responsible for the correlation between all organs and their systems for functioning of the organism as a whole. In the school of early familiarization with such multi-faceted concept, as the nervous system. Grade 4 – even young children who are unable to deeply understand the many complex scientific concepts.
Structural units
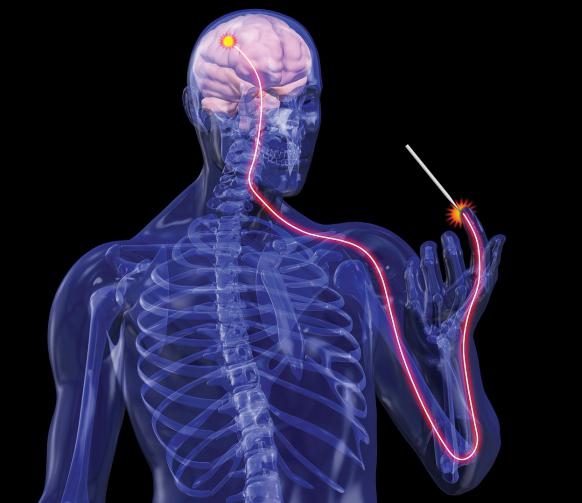
The Main structural and functional unit of the nervous system (NS) – neurons. They represent a complex excitable secreting cells with processes and perceive nervous energy, process it and transmit it to other cells. Neurons can also exert on target cells or modulating the braking effect. They are an integral part of bio - and chemorepulsion of the body. From a functional point of view, neurons are one of the foundations of the organization of the nervous system. They join several other levels (molecular, subcellular, synaptic, necletocny).
Neurons are composed of body (soma), long process (the axon) and a small branching processes (dendrites). In different parts of the nervous system they have a different shape and size. In some of them the length of the axon can reach 1.5 m. From one neuron moves up to 1000 dendrites. According to him, the excitation is propagated from the receptor to the cell body. Along the axon, the impulses are transmitted to the effector cells or other neurons.
In science there is the concept of "synapse". The axons of neurons, approaching the other cells start to branch and form numerous endings on them. Such places are called synapses. Their axons form not only on nerve cells. There are synapses on muscle fibers. These organs of the nervous system are present even in the cells of the endocrine glands and blood capillaries. The nerve fibers represent covered by glial sheaths of neuronal processes. They perform a conductive function.
Recommended
"Knowledge is light and ignorance is darkness": the value, meaning and alternatives
There are some sayings that would seem to need no explanation, such as “teaching & ndash; light and ignorance – darkness”. But some still do not understand their meaning. But not only for such people is written by our article. I...
What was invented by Mendeleev for the army. The history and fate of the invention
D. I. Mendeleev was a brilliant Russian scientist-polymath, who made many important discoveries in various fields of science and technology. Many people know that he is the author of “Fundamentals of chemistry" and the periodic law of chem...
The origin of the Slavs. The influence of different cultures
Slavs (under this name), according to some researchers, appeared in the story only in 6 century ad. However, the language of nationality bears the archaic features of the Indo-European community. This, in turn, suggests that the origin of the Slavs h...
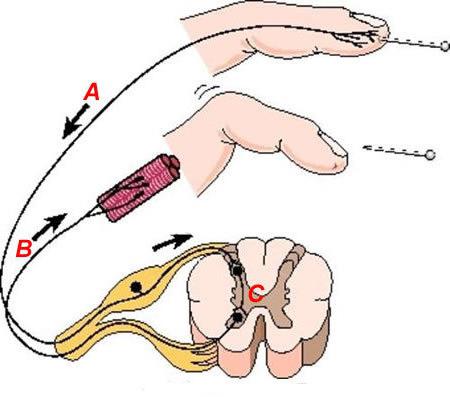
Nerve endings
This is a specialized education, located at the tips of processes of nerve fibers. They provide the transfer of information in the form of a pulse. Nerve endings are involved in the formation of the transmission and perception of end devices of different structural organization. On a functional purpose distinguish:
• the synapses that transmit nerve impulses between nerve cells.
• the receptors (afferent end), the guide information from the site of action of the factor of the internal or external environment;
• effectors that transmit the impulse from nerve cells to other tissues.
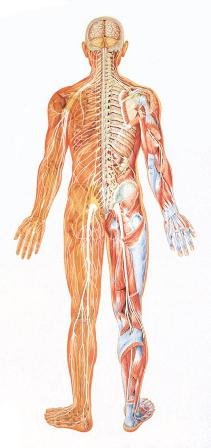
Nervous system
The Nervous system (NS) – the holistic combination of several interrelated structures. It promotes coordinated regulation of all organs and provides a response to the changing conditions. The human nervous system, photos of which are presented in the article connects the motor activity, sensitivity, and the work of other regulatory systems (immune, endocrine). The NA activity is associated with:
• anatomical penetration into all the organs and tissues;
• establishment and optimization of the relationship between the organism and the ambient environment (environmental, social);
• co-ordination of all metabolic processes;
• management of the organ systems.
Structure
Anatomy of the nervous system is very complex. There is plenty of structures, different in structure and purpose. Nervous system, photos of which indicate its penetration into all the organs and tissues of the body, plays an important role as the receiver of internal and external stimuli. This is a special sensory structures that are found in the so-called analyzers. They include special neural device that is able to perceive incoming information. These include the following:
• proprioreceptor collecting information about the state of the muscles, fascia, joints, bones;
• exteroretseptora, located in the skin, mucous membranes and organs of the senses, able to perceive received from the external environment irritants;
• interoreceptors, located in internal organs and tissues and is responsible for making biochemical changes.
The Main importance of the nervous system
The Work of the national Assembly is closely connected with the surrounding world and with the functioning of the body. With it comes the perception of information and its analysis. Thanks to her, is the recognition of stimuli of the internal organs and incoming data signals. The nervous system is responsible for reactions to the information. Thanks to its interaction with humoral mechanisms of regulation provided by the adaptability of man to the world.
The Value of the nervous system is the coordination of the individual parts of the body and maintain its homeostasis (equilibrium). Through her work is the adaptation of the organism to any changes, called adaptive behavior (state).
Basic functions NS
The function of the nervous system are quite numerous. These requirements consist of the following:
• regulationthe life of tissues, organs and systems in the normal mode;
• merging (integration) of the body;
• the preservation of the relationship of man with the environment;
• monitoring of the condition of individual organs and organism in General;
• ensure activation and maintenance of tone (working condition);
• defining activities of people and their mental health, which is the basis of social life.
The human Nervous system, a photo of which is presented above, provides the following thought processes:
• perception, learning and information processing;
• analysis and synthesis;
• formation of motivation;
• comparison with existing experience;
• goal setting and planning;
• correction operations (correction of errors);
• assessing performance;
• the formation of judgments, findings and conclusions, the General (abstract) concepts.
The Nervous system, in addition to the signal performs the trophic function. Thanks to her produced by the body of biologically active substances that ensure the livelihoods of the innervated organs. Organs that are deprived of such support, with time atrophy and die. The function of the nervous system is very important for a person. When changes to existing environmental conditions with their help, it is the adaptation of the organism to new circumstances.
The Processes occurring in the national Assembly
The human Nervous system, diagram is pretty simple and straightforward, is responsible for the interaction of organism and environment. To ensure such processes are carried out:
• transduction, which is a transformation of the irritation to the nervous excitement.
• transformation, which converts the incoming excitation with the same characteristics in the effluent with other properties;
• distribution of excitation in different directions;
• modeling, which is a build an image of irritation, replacing the source;
• modulation, changing the nervous system or its operations.
The Value of the human nervous system also consists in the interaction of the organism with the external environment. While there are various responses to all kinds of stimuli. Basic types of modulation:
• arousal (activation), which consists in increasing the activity of the nervous structure (this condition is dominant);
• inhibition, inhibition (inhibition), which consists in reducing the activity of nerve structure.
• temporary nervous connection, which represents the creation of new ways of excitation transfer;
• plastic changes, which is represented by sensitization (improvement of excitation transfer) and habitualy (deterioration of transmission);
• activation of the body, providing a reflex reaction of the human body.
Tasks NS
The Main tasks of the nervous system:
• Reception – capture changes in the internal or external environment. It is a sensory system with receptors and represents the perception of mechanical, thermal, chemical, electromagnetic and other types of irritants.
• Transduction-conversion (coding) of the received signal in nervous excitement, which is a stream of pulses with characteristics peculiar to the irritation.
• implementation of the holding, consisting in the delivery of excitation along the nerve paths to the necessary parts of the NS and to effectors (Executive bodies).
• Perception – creating nerve irritation model (build it touch the image). This process forms a subjective view of the world.
• Transformation-conversion excitation of the sensory in the effector. Its aim is the implementation of a response of the organism to changes of environment. Thus there is a downward transfer of excitation from the higher parts of Central nervous system to the downstream or in the PNS (working organs, tissues).
• Evaluation of the result of the activities of the national Assembly with the help of feedbacks and afferentation (transfer of sensory information).
Building NS
The human Nervous system, diagram of which is presented above, is divided in structural and functional terms. The work of the national Assembly cannot be fully comprehended without understanding the functions of its main species. Only by studying their purpose, it is possible to understand the complexity of the whole mechanism. The nervous system is divided into:
• Central (CNS), which carries out the reaction at different levels of complexity, called reflexes. She perceives the stimuli received from the environment and from the bodies. It includes the brain and spinal cord.
• Peripheral (PNS) connects the CNS with the organs and limbs. Its neurons are far away from the brain and spinal cord. It is not protected by bone, so prone to mechanical damage. Only due to the normal functioning of PNS possible coordination of human movements. This system is responsible for the response of the organism to danger and stress. Thanks to her, in such situations, quickens the pulse and increases the level of adrenaline. Diseases of the peripheral nervous system affect the Central nervous system.
The PNS is composed of bundles of nerve fibers. They go far beyond the dorsal andbrain and head to different bodies. They are called nerves. To the PNS are ganglia (nodes). They are a cluster of nerve cells.
Diseases of the peripheral nervous system is divided on these principles: topographic-anatomical, etiological, pathogenesis, pathomorphology. These include:
• radiculitis;
• plexitis;
• funiculitis;
• mono-, poly - and multiparity.
According to disease etiology they are divided into infectious (microbial and viral), toxic, allergic, dyscirculatory, dysmetabolic, traumatic, hereditary, idiopathic, compressing-coronary, vertebral. PNS disease can be primary (leprosy, leptospirosis, syphilis) and secondary (after childhood infections, mononucleosis, with nodular periarteritis). On pathomorphology and pathogenesis, they are divided into neuropathy (radiculopathy), neuritis (radiculitis) and neuralgia.
Properties of the nervous system
Reflex activity is largely determined by the properties of the nerve centers, which represent a set of structures of the CNS. Their coordinated activity provides for the regulation of various body functions or reflex acts. The nerve centers have several common properties determined by the structure and function of synaptic formations (the contact between neurons and other tissues):
• one-Sidedness of the process of excitation. It is distributed via the reflex arc in the same direction.
• Irradiation of excitation, namely that a considerable increase in the strength of the stimulus is the expansion of the area involved in this process of neurons.
• Summation of excitation. This process is facilitated by the presence of a great multitude of synaptic contacts.
• High fatigue. Prolonged repeated irritation is the weakening of the reflex response.
• Synaptic delay. Time reflex response depends entirely on the speed and the time of propagation of excitation across the synapse. In humans, one such latency is about 1 MS.
• Tone, which is the presence of background activity.
• Plasticity, which is the functional ability to significantly modify the overall picture of the reflex reactions.
• Convergence of neural signals, defining a physiological mechanism of the paths of afferent information (a constant flow of nerve impulses).
• Integration of cell functions in nerve centers.
• the Property is the dominant nerve of the hearth, characterized by increased excitability, the ability to excitation and summation.
• Cephalization of the nervous system consisting in movement, coordination of the body in the main departments of CNS and focusing in their function of regulation.
Article in other languages:
BE: https://tostpost.com/be/adukacyya/12192-znachenne-nervovay-s-stemy-funkcy-nervovay-s-stemy.html
KK: https://tostpost.com/kk/b-l-m/12195-m-n-zh-yke-zh-yes-funkciyalary-zh-yke-zh-yes.html
PL: https://tostpost.com/pl/edukacja/12186-warto-uk-adu-nerwowego-funkcje-uk-adu-nerwowego.html
PT: https://tostpost.com/pt/educa-o/12179-o-valor-do-sistema-nervoso-a-fun-o-do-sistema-nervoso.html
TR: https://tostpost.com/tr/e-itim/12197-de-er-sinir-sistemi-sinir-sistemi-fonksiyonu.html
UK: https://tostpost.com/uk/osv-ta/12190-znachennya-nervovo-sistemi-funkc-nervovo-sistemi.html

Alin Trodden - author of the article, editor
"Hi, I'm Alin Trodden. I write texts, read books, and look for impressions. And I'm not bad at telling you about it. I am always happy to participate in interesting projects."
Related News
The Admiralty building, Saint Petersburg: history, description
the St. Petersburg Admiralty building is one of the most recognizable symbols of the city. It was built under Peter I and since then has been used as the location of the collegiums of ministries and other state institutions.the Br...
Ravenous appetite - is... meaning of the idiom, synonyms
for anybody not a secret that in the Russian language, a large spread of different turns of phrase, the meaning of which is very difficult to understand. Ravenous appetite – a vivid example is the mysterious stable structure...
A four-chambered heart of amphibians and reptiles: examples
Our planet is densely populated by animals of different classes, groups and types. Scientists are studying their structure and functional significance of individual organs. About what the heart in amphibians and reptiles, read the...
The thermodynamic equilibrium of the biological system
is called Thermodynamics the branch of physics that studies heat and the principles of its distribution throughout the volume of a substance or a particular environment. This discipline is based on some General universal principle...
Essay: the image of the play Ranevskaya in "the Cherry orchard"
“the Cherry orchard» — the last and decisive contribution of Chekhov in Russian drama. This piece was the final of his career, but it had developed brand new styles. The image of him in the play «the Cherry...
The digestive system of birds. The internal structure of birds
key features of the admission of substances, their transformation, and excretion of undigested residues from the body performs a digestive system. Birds, being animals adapted for flight, have certain features of the internal stru...




















Comments (0)
This article has no comment, be the first!