Now - 02:37:43
Genetic information storage and transmission. Genetic code. DNA chain
After the discovery of the principle of molecular structure of substances such as DNA in 1953, began developing molecular biology. Later in the research process Scientists figured out how rekomenduetsa DNA, composition and how it works in our human genome.
Every day occur at the molecular level of complex processes. How to construct a DNA molecule what it is? And what is the role of in the cell the DNA molecule? Describe in detail about all the processes taking place inside a double chain.
What is genetic information?
So, where did it all begin? ESche in 1868 found nucleic acid in the nuclei of bacteria. And in 1928 N. Koltsov put forward the theory that it is in the DNA encoded all of the genetic information of a living organism. Then, George. Watson and Crick found the model of all now known of the DNA helix in 1953, for which has earned recognition and awards — Nobel prize.
What is the General DNA? This substance consists of 2 United filaments, or spirals. Part of that chain with Certain information is called the genome.

In DNA stores all the information about what proteins will be formed and in what order. Macromolecule DNA — a material carrier is incredibly Surround information, which is recorded by a strict sequence of individual building blocks-nucleotides. All 4 nucleotides, they complement each other chemically and geometrically. This add-on principle or complementarity in science will be described later. This rule plays a key role in the encoding and decoding of genetic information.
Recommended
"Knowledge is light and ignorance is darkness": the value, meaning and alternatives
There are some sayings that would seem to need no explanation, such as “teaching & ndash; light and ignorance – darkness”. But some still do not understand their meaning. But not only for such people is written by our article. I...
What was invented by Mendeleev for the army. The history and fate of the invention
D. I. Mendeleev was a brilliant Russian scientist-polymath, who made many important discoveries in various fields of science and technology. Many people know that he is the author of “Fundamentals of chemistry" and the periodic law of chem...
The origin of the Slavs. The influence of different cultures
Slavs (under this name), according to some researchers, appeared in the story only in 6 century ad. However, the language of nationality bears the archaic features of the Indo-European community. This, in turn, suggests that the origin of the Slavs h...
As the DNA strand is incredibly long, the repetitions in this sequence does not happen. Every living being has its own unique DNA sequence.
DNA Function
The functions of the deoxyribonucleic acids are the storage of genetic information and transfer to offspring. Without this feature, the genome of the species could be preserved and developed for millennia. Organisms that have undergone a Serious gene mutations often do not survive or lose their ability to produce offspring. This happens the natural protection from degeneration. the
Else one essential feature — implementation of the stored information. The cell cannot create a single vital protein without the instructions, which are stored in a double chain.
Nucleic acids
Now it is authentically known, what are the very nucleotides — the building blocks of DNA. It is composed of 3 components:
- Phosphoric acid.
- Nitrogenous base. Pyrimidine base — that have only one ring. These include thymine and cytosine. A purine base, a composition which contains 2 rings. It is a guanine and an adenine.
- Sucrose. Composed of DNA — deoxyribose, RNA-ribose.
The Number of nucleotides is always equal to the number of bases. In special laboratories of the cleaved nucleotide and sense of nitrogenous base. So studying the individual properties of these nucleotides and possible mutations of them.
Levels of organization of genetic information
Share 3 levels of organization: genetic, chromosomal and genomic. All information needed for the synthesis of new protein, contains a small portion of the chain — the gene. That is, the gene is considered to be the lowest and the simplest level of encoding information.
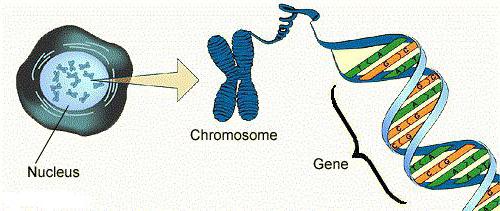
Genes, in turn, assembled into chromosomes. Due to this arrangement the carrier of the hereditary material of the group of signs on Certain the laws are interleaved and transmitted from one generation to the next. It should be noted, genes in the body are so many, but the information is not lost, even when many times rekomenduetsya.
There are several types of genes:
- On a functional purpose distinguish 2 types: structural and regulatory sequence;
- To influence the processes occurring in the cell are distinguished: supervielle, lethal, conditional lethal genes, and mutator genes and antimatter.
Genes Are arranged along chromosomes in a linear order. In the chromosomes of information focused not random, there is a certain order. There is even a map that reflects the positions or loci of genes. For example, it is known that in chromosome No. 18 encrypted data about eye color Child.
What is a genome? So called the totality of the nucleotide sequences in the cell of the organism. Genome characterizes a whole species and not an individual.
What isthe human genetic code?
The fact that the whole enormous potential for human development is laid in the period of conception. All the hereditary information, which is required for zygote development and growth of Child after the birth, encoded in the genes. Stretches of DNA are the main carriers of hereditary information.
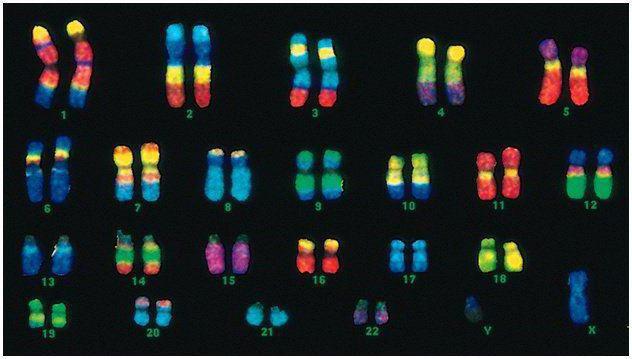
In humans, 46 chromosomes, or 22 pairs of somatic plus one gender determining chromosome from each parent. This diploid set of chromosomes encodes all the physical appearance of the man, his mental and physical ability and predisposition to diseases. Somatic chromosomes are outwardly indistinguishable, but they carry different information, since one of them from father, other from mother.
Men's code differs from the female of the last pair of chromosomes-XY. The female diploid set — the last pair is XX. Men Get one X chromosome from her biological mother, and then she Passed daughters. Sexual y-chromosome Passed boys.
Human Chromosome vary greatly in size. For example, the smallest pair of chromosomes - No. 17. And the biggest pair 1 and 3.
The diameter of the double helix in humans is only 2 nm. DNA is so tightly twisted that it fits in a small nucleus of the cell, while length will reach 2 meters if spin. Length of spiral — hundreds of millions of nucleotides.
How is the genetic code?
So, what is the role of in the cell the DNA molecule in the division? Genes — carry genetic information inside every cell in the body. To send your code to the child body, many creatures share the My DNA into 2 identical spirals. This is called replication. In the process of DNA replication rasplatitsya and special “machine” complement each chain. After the split of the genetic spiral, begins to divide, the nucleus and all the organelles, and then the entire cage.
But another process of the transfer of genes - sexual. The signs father and mother are shuffled, the new code contains genetic information from both parents.
The Storage and transmission of genetic information possible because of the complex organization of the DNA helix. After all, as we said, the structure of proteins encrypted in the genes. Once created at the time of conception, the code for the whole of life is to copy itself. A karyotype (a chromosome) is not changed during the updates of the cells of the organs. Transmission of information using sexual gametes-male and female.
Send your information to the offspring is not able only viruses containing a single chain RNA. So to reproduce, they need cells of a human or animal.
The Realization of hereditary information
In the cell nucleus is constantly undergoing important processes. All information recorded in the chromosomes, is used to build proteins from amino acids. But the DNA never leaves the nucleus, so it needs the help of another important connection = RNA. Just RNA is able to penetrate through the membrane of the nucleus and interact with DNA.
Through interaction of DNA and 3 types of RNA is the implementation of all encoded information. At what level is the implementation of genetic information? All interactions occur at the level of nucleotides. RNA copies the portion of the DNA chain and brings the copy to the ribosome. Here begins the synthesis of the nucleotides of a new molecule.
In order For mRNA to be able to copy the necessary part of the chain, the spiral is set, and then, upon completion of the conversion, is restored again. And this process can occur simultaneously on the 2 sides of 1 chromosome.
Principle of complementarity
The Helix DNA consists of 4 nucleotides is adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), thymine (T). They are connected by hydrogen bonds according to the rule of complementarity. The work of E. Chargaff helped to establish this rule, because Scientist noticed some regularities in the behavior of these substances. E. Chargaff revealed that the mole ratio of adenine to thymine is equal to one. And similarly, the ratio of guanine to cytosine is always equal to one.
On the basis of his work, geneticists have established a rule of interaction of nucleotides. The rule of complementarity States that adenine connects only with thymine, and guanine with cytosine. During decoding of the spiral and the synthesis of new protein in the ribosome is a rule of alternation helps you quickly find the amino acid that is attached to transfer RNA.
RNA and its types
What is genetic information? This is the sequence of nucleotides in the double chains of DNA. And what is RNA? In Than is work? RNA, or ribonucleic acid, helps to extract information from DNA, to decode
In summary there are 3 kinds of RNA. Each of them performs strictly its function.
- Information (mRNA), or Else is called a matrix. She walks right into the center of the cell, into the nucleus. Finds in one of the chromosomes the genetic material necessary for building protein and copies one side of a double chain. Reproduction takes place again on the principle of complementarity.
- Transport — is a small molecule, which on one side decoders-nucleotides, and on the other side of the appropriate main code amino acids. Task tRNA — to bring in “shop”, that is, in the ribosome, where the synthesis of the essential amino acid.
- RRNA-ribosomal. It controls the amount of protein that is produced. Consists of 2 parts amino acid and peptide area.
The Only difference when decoding — in RNA there is no thymine. Is present instead of thymine there is uracil. But then, in the process of protein synthesis, TRNA while still correctly sets all the amino acids. If there are any failures in the decoding information, then the mutation occurs.
Repair damaged DNA molecules
The recovery Process Damaged double chain is called reparation. In the process of reparation Damaged genes deleted.

Then the required sequence of elements is exactly reproduced and cuts back to the same place on the circuit where it was extracted. This is due to special chemicals-enzymes.
Why there are mutations?
Why are some genes begin to mutate and cease to perform their function — storing vital hereditary information? This is due to errors when decoding. For example, if adenine is accidentally Replaced to thymine.
There are also chromosomal and genomic mutations. Chromosomal mutations occur, if the sites of hereditary information drop out, doubled or even transferred and inserted into another chromosome.

Genomic mutations are the most Serious. Their reason is the change in the number of chromosomes. That is, when instead of the pair — the diploid set is present in the karyotype triploid set.
The Most famous example triploid mutation is down syndrome, in which the personal set of chromosomes 47. These children formed 3 chromosomes in the 21-th pair.
Also Known for this mutation, as polyploidy. But polyploidy is found only in plants.
Article in other languages:

Alin Trodden - author of the article, editor
"Hi, I'm Alin Trodden. I write texts, read books, and look for impressions. And I'm not bad at telling you about it. I am always happy to participate in interesting projects."
Related News
What "the fuss"? Value synonyms, interpretation
let's Talk about the phenomenon, without which no cost, no detective, and in life it occurs quite often, and erupted usually because of some trifles. Answer the question about what "the fuss".Origin and full of expressionFirst I m...
Anton Chekhov, "the Cherry orchard": an essay in literature
To comprehend the meaning of the last plays of Anton Chekhov appeal and today, theatre activists, critics and ordinary viewers. What is the artistic value of «the Cherry orchard»? This piece was interesting not only co...
The structure of scientific knowledge – what it is
Those who are faced with science and its peculiarities in the beginning need to understand what is the structure of scientific knowledge and what it implies. And, oddly enough, any knowledge is possible in some way to classify cer...
Discoveries and inventions of the New time
Some of the most significant discoveries occurred during periods that are called New and the Newest time. When does the count of these periods? What discoveries were made during this time?the Beginning of a New timeNew time is cal...
Who is Bolivar fought for the independence or a despotic leader?
the Brave hero of numerous novels and biographies, fierce fighter for the independence of South America, the first President of Venezuela, the man after whom is named the whole state - that's who chart.Originsit All started in the...
The Paris peace conference of 1919-1920.
After the final victory over Germany in the First world war, the victorious countries began to plan the future structure of the world. It was necessary to sign a peace agreement and to legitimize the territorial changes occurred. ...






















Comments (0)
This article has no comment, be the first!