Now - 10:16:32
Transamination of amino acids: definition, importance and characteristics
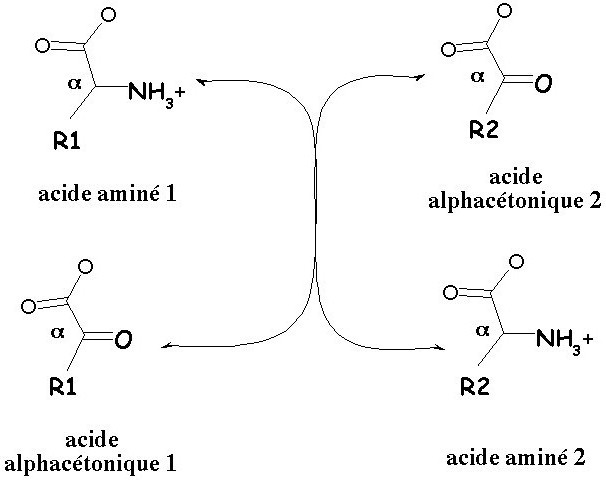
Transamination of amino acids are the processes of intermolecular transfer from a starting material of the amino group to a ketoacid without the formation of ammonia. Let's examine the specifics of this reaction and its biological significance.
History of discovery
The Reaction of transamination of amino acids was opened by the Soviet chemists-Krizman and Brainstem in 1927. Scientists worked on the process of deamination of glutamic acid in muscle tissue and found that as you add to the homogenate of the muscle tissue, pyruvic and glutamic acids, alanine is formed and α-ketoglutaric acid. The uniqueness of the discovery was that the process was not accompanied by the formation of ammonia. In experiments they found out that the transamination of amino acids is a reversible process.
The reactions as catalysts were used specific enzymes, which were named aminophenazone (transaminasemia).
Features
Amino acids involved in the transamination, can be monocarboxylic compounds. In laboratory studies it was found that the transamination of asparagine and glutamine with keto acids occurs in the tissues of animals.
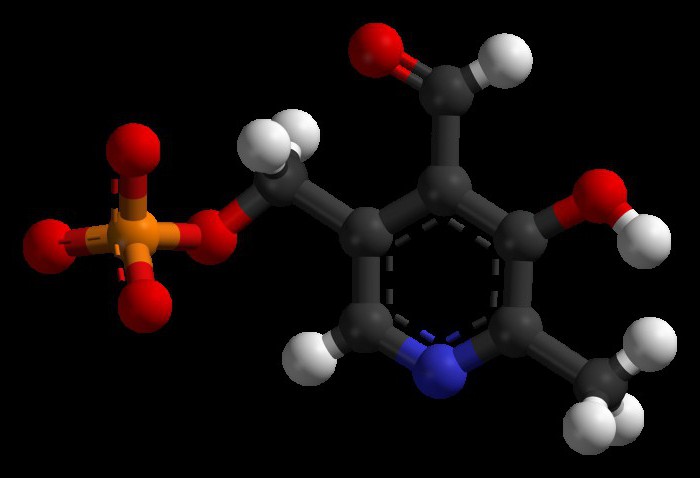
Active participation in the transfer of an amino group takes pyridoxal phosphate is a coenzyme of transaminases. In the process of interaction it is formed from piridoksalfosfat. As a catalyst of such a process are the enzymes: oxidase, pyridoxamine.
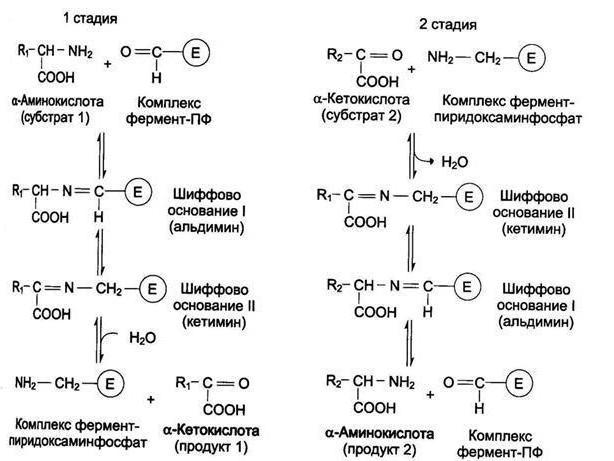
Reaction Mechanism
Transamination of amino acids was explained by Soviet scientists Braunstein and Shemyakin. All transaminases is pyridoxal phosphate coenzyme. Reaction transaminirovania that it accelerates, similar in mechanism. The process proceeds in two stages. First, pyridoxal phosphate takes from the amino acid functional group, the resulting ketoacid and pyridoxamine. In the second stage, it reacts with α-ketoacid with, as the end products formed pyridoxal phosphate, the corresponding ketoacid. In such interactions pyridoxal phosphate is a carrier of amino groups.
Recommended
"Knowledge is light and ignorance is darkness": the value, meaning and alternatives
There are some sayings that would seem to need no explanation, such as “teaching & ndash; light and ignorance – darkness”. But some still do not understand their meaning. But not only for such people is written by our article. I...
What was invented by Mendeleev for the army. The history and fate of the invention
D. I. Mendeleev was a brilliant Russian scientist-polymath, who made many important discoveries in various fields of science and technology. Many people know that he is the author of “Fundamentals of chemistry" and the periodic law of chem...
The origin of the Slavs. The influence of different cultures
Slavs (under this name), according to some researchers, appeared in the story only in 6 century ad. However, the language of nationality bears the archaic features of the Indo-European community. This, in turn, suggests that the origin of the Slavs h...
Transamination of amino acids by this mechanism was confirmed by methods of spectral analysis. Currently, there is a new evidence of the presence of such mechanism in living beings.
The Value in the exchange process
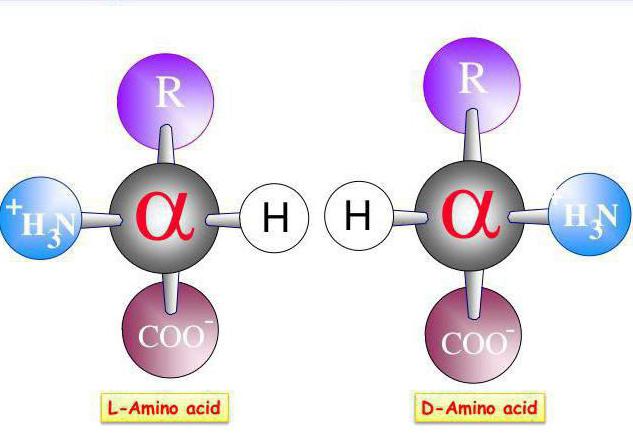
What is the role of transamination of amino acids? The value of this process is sufficiently large. These reactions are widespread in plants and microorganisms in animal tissues due to its high resistance to chemical, physical, biological factors, the absolute stereochemical specificity against D - and L-amino acids.
The Biological significance of transamination of amino acids were analyzed by many scientists. He was the subject of detailed studies in amino acid metabolic processes. In the course of research was the hypothesis about the possibility of the process of transamination of amino acids with transmetilirovania. Euler found that in animal tissues from amino acids with a high speed dezaminiruet only L-glutamic acid, a catalyst of a process is glutamatdekarboksilazy.
The Processes of deamination and transamination of glutamic acid are reversible reactions.
Clinical significance
How to use the transamination of amino acids? The biological significance of this process lies in the possibility of conducting clinical trials. For example, blood serum of a healthy person has between 15 to 20 units of transaminases. In the case of organic lesions of the tissues is observed destruction of cells that results in the release of transaminases into the blood from the lesion.
In the case of myocardial infarction within 3 hours the level of aspartate aminotransferase is increased to 500 units.
How to use the transamination of amino acids? Biochemistry involves conducting transaminase test, the results of which the patient is diagnosed, select the effective methods of treatment of this disease.
For diagnostic purposes in the clinic diseases use special sets of chemicals, to detect the activity of lactate dehydrogenase, creatine kinase, transaminases.
Hypertransaminasemia observed in diseases of the kidney, liver, pancreas, and in the case of acute poisoning with carbon tetrachloride.
Transamination and deamination of amino acids used in modern diagnostics to detect acute infections of the liver. This is due to the sharp increase in alanine aminotransferase in certain liver problems.
Members of transamination
A Special role in this process is glutamic acid. Widespread in plant and animal tissues, stereochemical specificity for amino acids, the catalytic activity has made her a subject of study in researchlaboratories. All natural amino acids (except methionine) interacts with α-ketoglutaric acid during the transamination, as a result of keto - glutamic acid. It is exposed under the action of glutamatdekarboksilazy the deamination.
Options oxidative deamination
There are direct and indirect types of this process. Direct deamination involves the use as catalyst of one of the enzyme-product interactions are the ketoacid and ammonia. This process can occur aerobically, suggesting the presence of oxygen, or anaerobic one (without oxygen molecules).
Features of oxidative deamination
As catalysts In the aerobic process are the D-amino acid oxidase, and the coenzyme oxidase are L-amino acids. These substances are present in the human body, but they show minimal activity.
A variant of the Anaerobic oxidative deamination possible for glutamic acid, as the catalyst serves glutamatdekarboksilazy. This enzyme is present in mitochondria of all living organisms.
In the indirect oxidative deamination there are two stages. First, the amino group is transferred from the initial molecule to closedeye a new keto - and amino acids. Further, closely specific ways metaboliziruet, involved in the tricarboxylic acid cycle and in tissue respiration, the end products are water and carbon dioxide. In the case of starvation the carbon skeleton of amino acids glûkogennymi will be used for education in the gluconeogenesis of glucose molecules.
The Second stage involves cleavage of the amino group by deamination. In the human body such a process is possible only for glutamic acid. As a result of this interaction is formed by α-ketoglutaric acid and ammonia.
Conclusion
Determination of the activity of two enzymes, the transamination of alanine aminotransferase aspartatamintransferazy and has found application in medicine. These enzymes can reversibly interact with α-ketoglutaric acid, transferred to it from amino acids, functional amino groups, forming catasetinae and glutamic acid. Despite the fact that the activity of these enzymes is increased in diseases of the heart muscle and liver, the maximum activity found in the blood serum for AST and ALT in hepatitis.
Amino acids are critical in the synthesis of protein molecules and the formation of many other biological active compounds that can regulate the body's metabolic processes: hormones, neurotransmitters. In addition, they are donors of nitrogen atoms in the synthesis of nonprotein nitrogen-containing substances, including choline, creatine.
Catabolism amino acids can be used as a source of energy for the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate. The special value of energy function of amino acids is in the process of starvation and diabetes. Amino acid metabolism allows you to establish links between the numerous chemical reactions occurring in a living organism.
The human body contains about 35 grams of free amino acids and the blood of their content is 3565 mg/DL. A large number of them enters the body from food, in addition, they have in their own tissues, can also be formed from carbohydrates.
In many cells (except erythrocytes), they are used not only for protein synthesis but also for the formation of purine, pyrimidine nucleotides, obtaining biogenic amines, phospholipids membranes.
The day in the human body into amino acids breaks down approximately 400 g of protein compounds, and about the same number, the process is reversed.
Tissue proteins are not able to perform in the case of catabolism of the cost of amino acids on the synthesis of other organic compounds.
In the evolution of mankind lost the ability to self-synthesis of many amino acids, therefore, to ensure in full volume their body needs to obtain these nitrogen-containing compounds with food. Chemical processes involving amino acids, and today is the object of study by chemists and physicians.
Article in other languages:
AR: https://tostpost.com/ar/education/17699-transamination.html
HI: https://tostpost.com/hi/education/19356-transamination.html
JA: https://tostpost.com/ja/education/17374-transamination.html
TR: https://tostpost.com/tr/e-itim/30777-transamination-amino-asitler-tan-m-nemi-ve-zellikleri.html

Alin Trodden - author of the article, editor
"Hi, I'm Alin Trodden. I write texts, read books, and look for impressions. And I'm not bad at telling you about it. I am always happy to participate in interesting projects."
Related News
"Blood with milk": the meaning of the idiom and the interpretation
Consider the meaning of the idiom “the blood milk” and talk about the women who embody its meaning in all its glory.Significancetalk about a healthy complexion. And last in this sense can be neither gray nor yellow, it...
Uncrowned Queen of England lady Jane grey: biography, life history and interesting facts
Lady Jane grey's fate gave only 17 years of life. But no! Grandniece of Henry VIII – king of England - he paid with his life for what was related to the famous old Tudor. In history she is known as the uncrowned Queen. What ...
The mechanism of action of enzymes
Enzymes (enzymes) are high - molecular organic compounds of protein nature, which perform in the body as a biological catalysts. the Mechanism of action of enzymes. elucidation of the mechanisms underlying the catalytic action of ...
The world of birds: little dove
the pigeon dazzling variety of species that differ in size, shape and color of plumage. Large breeds of pigeons reach the size of an adult chicken, but a small – little more than a Sparrow. pigeons are trusting to human and ...
English idioms with examples and meanings
to create a master palette, you need only three colors: red, yellow, blue. Mixing them, we get the so-called intermediate: green, orange and purple. And then what? The farther, the more colors and shades, without which life &ndash...
Political risk - what is it? Concept, types, examples
currently such a phrase as "political risk" found in all media if the publication is devoted to the problems of commercial activity. Now every investor, placing capital, has experience in the markets, skills of interaction with ot...




















Comments (0)
This article has no comment, be the first!